Source: Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
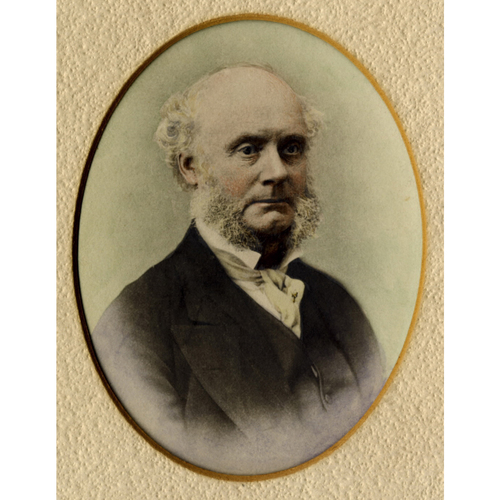
STREET, THOMAS CLARK (Clarke), lawyer, businessman, and politician; b. probably in 1814, son of Samuel Street* and Abigail Ransome; d. unmarried, 6 Sept. 1872, at Chippawa, Ont.
Thomas Clark Street’s father, Samuel, a United Empire Loyalist of English descent, owned, in partnership with Thomas Clark*, several grist and sawmills in the Niagara area. When Clark died in 1837, Street took these over and expanded into textile milling. His son, Thomas Clark, studied law in Toronto under Christopher Hagerman* and William Henry Draper, and was called to the bar in 1838. He returned to Chippawa to practise law but became more of a businessman than a lawyer. When his father died in 1844 he inherited “a liberal fortune” which he thereafter managed with considerable success. He later became a director of the Niagara Falls. Suspension Bridge Company and when he died he was president of the firm. He also served as president of the Gore Bank from 1862 to 1868 and was a director of the British American Assurance Company, the Canadian Bank of Commerce, and the Bank of Upper Canada. He invested in stock, owning shares in a number of financial and transportation companies.
Like many of his business colleagues, Street invested heavily in land and mortgages. Before the secret ballot this form of business involvement was of considerable political utility. As the Niagara Mail in St Catharines commented in 1851 when Street first ran for office, his principal assets were “his money and his mortgages.” He was elected to the Legislative Assembly for Welland in 1851 but defeated in an unusually violent contest in 1854. Elected again in 1861, he sat for Welland in the union and later the federal parliaments until his death. Street was a lifelong Conservative. In 1851 he had campaigned as an independent, calling himself a “Constitutional Reformer,” but was regarded by Reformers as a Family Compact Tory.
Although his political career was long and seemingly placid and took second place to his business interests, Street was an important politician. Men like Street did not sit in parliament as mindless supporters of a particular leader; he was not dependent on his party for campaign funds, and he needed neither his sessional indemnity nor a patronage post. His own economic interests were pushed, and he often acted with independence and courage. A strong supporter of representation by population, which he advocated not for love of the measure but because of what he feared would happen without it, he refused to enter the cabinet in 1862 when asked by John A. Macdonald* because it had not accepted that policy. He also supported the unpopular bill presented by Richard William Scott* in 1863 regarding separate schools. His weight was recognized by Macdonald, who assured him in 1867 that a place was reserved for him in the Senate: “[As] vacancies will be annually occurring you can, when you are wearied of well doing in the Commons, find your way to the dignified retirement of our House of Peers.”
Street was very much an aristocrat, and in 1860 “entertained [the Prince of Wales] on a scale of magnificence seldom equalled in any colony of England.” A member of the Church of England, he served as trustee of the University of Trinity College in Toronto. He was a lieutenant-colonel in the Welland militia and a justice of the peace. He died in 1872 in Chippawa shortly after being re-elected to the House of Commons by acclamation. He left an estate valued at between $3,000,000 and $4,000,000, often regarded as the largest in Ontario at that time.
PAC, MG 26, A (Macdonald papers), 338, 513. PAO, W. H. Merritt papers; Samuel Street papers. Gazette (Montreal), 1872. Globe (Toronto), 1861–72. Leader (Toronto), 1872. Mail (Toronto), 1872. Niagara Mail, 1851–61. Can. directory of parliament (Johnson). Can. part. comp., 1872. M. F. Campbell, Niagara: hinge of the golden arc (Toronto, 1958). Cornell, Alignment of political groups. Creighton, Macdonald, young politician. Ross and Trigge, History of the Canadian Bank of Commerce, II. Swainson, “Personnel of politics.”
Cite This Article
Donald Swainson, “STREET, THOMAS CLARK (Clarke),” in Dictionary of Canadian Biography, vol. 10, University of Toronto/Université Laval, 2003–, accessed January 1, 2026, https://www.biographi.ca/en/bio/street_thomas_clark_10E.html.
The citation above shows the format for footnotes and endnotes according to the Chicago manual of style (16th edition). Information to be used in other citation formats:
| Permalink: | https://www.biographi.ca/en/bio/street_thomas_clark_10E.html |
| Author of Article: | Donald Swainson |
| Title of Article: | STREET, THOMAS CLARK (Clarke) |
| Publication Name: | Dictionary of Canadian Biography, vol. 10 |
| Publisher: | University of Toronto/Université Laval |
| Year of publication: | 1972 |
| Year of revision: | 1972 |
| Access Date: | January 1, 2026 |




